
WeightWatchers, now known as WW International, has long been a household name in weight management. Founded in 1963, the company built its reputation on a community-driven approach to dieting, emphasizing calorie counting, portion control, and group support. At its peak, WeightWatchers boasted millions of members worldwide, valued at over $7 billion. However, on May 6, 2025, the company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in Delaware, citing $1.5 billion in debt and plans to restructure under creditor control.
The decline of WeightWatchers can be attributed to several factors. The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted in-person meetings, a cornerstone of the Weight Watchers model, leading to a decline in membership. Additionally, the rise of pharmaceutical weight loss solutions, particularly GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro, has shifted consumer preferences toward medical interventions. These drugs offer significant weight loss results with less effort, making traditional dieting programs less appealing. As a result, WeightWatchers struggled to compete in a market increasingly dominated by pharmaceutical solutions.
The Rise of GLP-1 Drugs
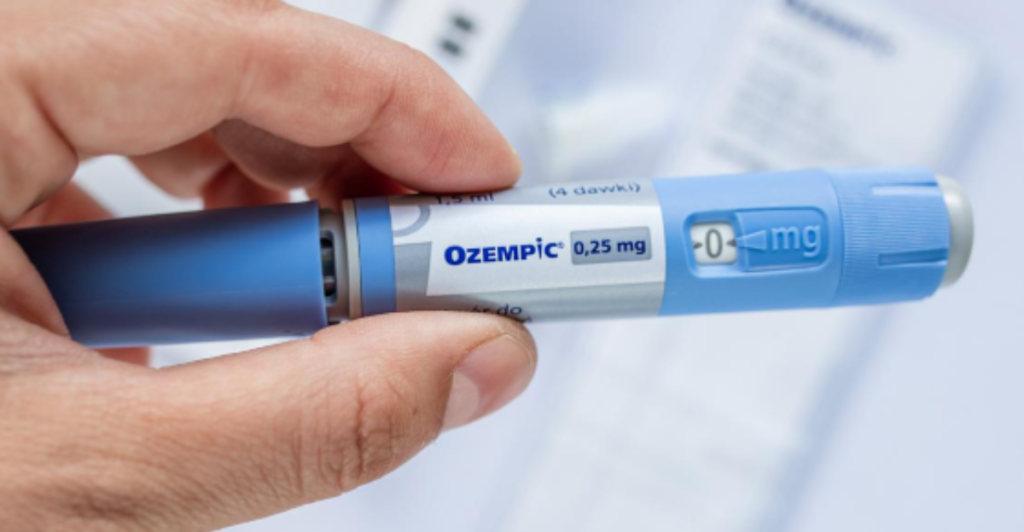
GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide (Ozempic) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro), were initially developed to manage type 2 diabetes by mimicking the glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, which regulates blood sugar levels. However, these drugs have also been found to promote significant weight loss by suppressing appetite and slowing gastric emptying. Clinical trials have demonstrated that patients using GLP-1 drugs can lose an average of 15-20% of their body weight over 68-78 weeks.
The effectiveness of GLP-1 drugs has led to their widespread adoption for weight loss, even among individuals without diabetes. The convenience of a once-weekly injection and the promise of substantial weight loss have made these drugs a popular alternative to traditional dieting methods. As a result, programs like WeightWatchers have seen a decline in membership as consumers opt for pharmaceutical solutions that offer quicker results with less lifestyle modification.
Personal Stories Reflecting a Broader Trend

The shift toward pharmaceutical weight loss solutions is evident in personal accounts shared by individuals who have used GLP-1 drugs. For instance, Gemma Kelly, a mother of two, reported losing 3.5 stone (approximately 49 pounds) in two months using Mounjaro, without engaging in exercise. Similarly, Bethany Diana, a 27-year-old from the UK, lost six stone (about 84 pounds) and dropped from a size 18 to a size 10 after using Mounjaro.
These stories highlight the appeal of GLP-1 drugs: rapid and significant weight loss with minimal lifestyle changes. However, they also underscore potential downsides, such as sagging skin and the need for ongoing medication to maintain results. Despite these concerns, the effectiveness of GLP-1 drugs continues to draw individuals away from traditional weight loss programs like Weight Watchers, contributing to the company’s decline.
Financial Struggles and Market Shifts

WeightWatchers’ financial troubles are not solely due to the rise of GLP-1 drugs. The company has also faced challenges adapting to digital trends and competing with free or low-cost fitness and nutrition apps. Despite efforts to modernize its platform and incorporate digital tools, WeightWatchers has struggled to retain its customer base. The company’s stock has plummeted, and its valuation has decreased significantly from its peak.
The broader market shift toward pharmaceutical solutions for weight loss has further exacerbated WeightWatchers’ decline. As consumers increasingly seek medical interventions, traditional dieting programs must find ways to adapt and remain relevant in a rapidly changing industry.
Understanding the Mechanism of GLP-1 Drugs
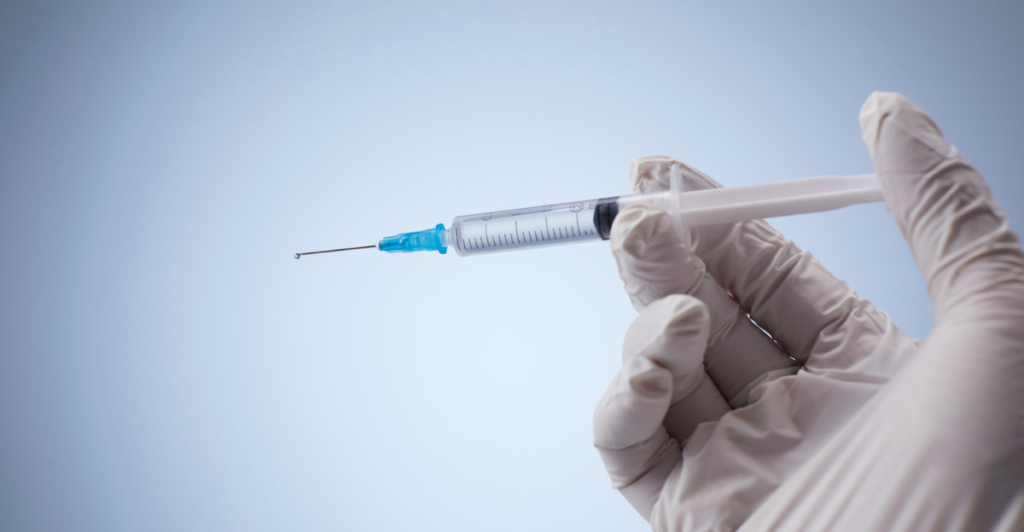
GLP-1 receptor agonists work by mimicking the action of the glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, which is released in the gut in response to food intake. This hormone stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety. By enhancing these effects, GLP-1 drugs help individuals feel full longer and reduce overall calorie intake, leading to weight loss.
These drugs are typically administered via injection, with dosing schedules varying from daily to weekly, depending on the specific medication. While initially approved for managing type 2 diabetes, the significant weight loss observed in patients has led to their approval for treating obesity in individuals without diabetes. The dual benefits of blood sugar regulation and weight loss have made GLP-1 drugs a compelling option for many seeking to manage their weight.
Side Effects and Health Considerations

While GLP-1 drugs offer promising weight loss results, they are not without potential side effects. Common adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. More serious risks, though less common, involve pancreatitis, gallbladder disease, kidney problems, and potential thyroid tumors.
Additionally, rapid weight loss associated with these drugs can lead to physical changes such as sagging skin and facial volume loss, colloquially known as “Ozempic face.” While not medically dangerous, these aesthetic concerns can impact individuals’ satisfaction with their weight loss results. Patients must consult healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks of GLP-1 therapy and ensure appropriate treatment monitoring.
Accessibility and Cost Challenges

The high cost of GLP-1 drugs presents a significant barrier to access for many individuals. Prices can range from $800 to $1,500 per month without insurance coverage. Insurance coverage for these medications is inconsistent, with many plans not covering them for weight loss purposes. Medicare, for example, does not currently cover GLP-1 drugs for weight management, though it may cover them for diabetes treatment.
These financial challenges limit the accessibility of GLP-1 drugs to a broader population, raising concerns about health equity. Individuals without the means to afford these medications may be unable to benefit from their weight loss effects, highlighting the need for more affordable and inclusive weight management solutions.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
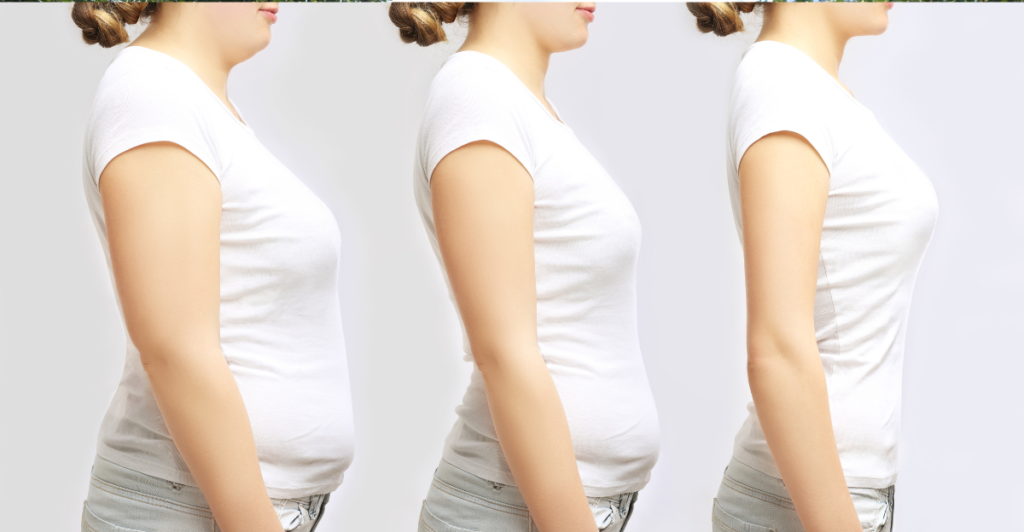

While GLP-1 drugs can facilitate weight loss, they are most effective with lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular physical activity. Relying solely on medication without addressing underlying behavioral factors may lead to weight regain once the medication is discontinued. Healthcare providers emphasize the importance of comprehensive weight management plans, including pharmacological and lifestyle interventions.
Programs like WeightWatchers have traditionally focused on these lifestyle components, offering support and education to help individuals make sustainable changes. As the weight loss industry evolves, integrating medical treatments with behavioral support may offer a more holistic approach to weight management.
The Future of Weight Management

The landscape of weight management is shifting, with pharmaceutical interventions playing an increasingly prominent role. However, the importance of lifestyle factors in achieving and maintaining weight loss cannot be overstated. Future approaches may involve a combination of medical treatments and behavioral support to address the multifaceted nature of obesity.
As the industry adapts, companies like WeightWatchers may need to evolve their models to incorporate medical options while retaining their strengths in community support and lifestyle education. Collaboration between healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and traditional weight loss programs could lead to more comprehensive and effective solutions for individuals seeking to manage their weight.
Economic Implications for American Households

The rise of expensive pharmaceutical weight loss treatments has significant financial implications for American households. With monthly costs ranging from $800 to $1,500, GLP-1 drugs can strain household budgets, especially for those without insurance coverage. The lack of consistent insurance reimbursement further exacerbates this issue, potentially leading individuals to forgo treatment or incur debt to afford medication.
SANEMD
This financial burden underscores the need for more affordable and accessible weight management options. Policymakers and healthcare stakeholders must consider reducing costs and expanding coverage for effective treatments. Ensuring all individuals have access to comprehensive weight management solutions is essential for addressing the obesity epidemic and promoting public health.
Discover more trending stories and Follow us to keep inspiration flowing to your feed!
Craving more home and lifestyle inspiration? Hit Follow to keep the creativity flowing, and let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
