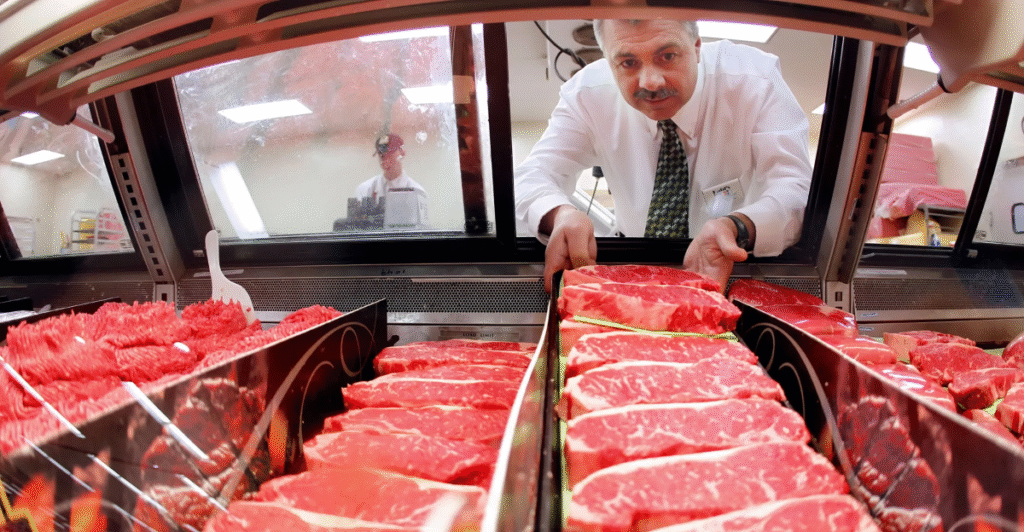

In 2025, U.S. beef prices have reached unprecedented levels, significantly impacting consumers nationwide. Ground beef now averages $5.79 per pound, a 13% increase from the previous year. Sirloin steaks are nearing $12 per pound, just below the record high of $12.01 set in late 2024. This surge is primarily attributed to the U.S. cattle herd declining to 86.7 million head, the lowest since 1951, due to prolonged droughts and rising feed costs.
Labor shortages and increased insurance expenses have further strained the supply chain. Trade disruptions, including tariffs on beef imports from Mexico, Brazil, and Canada, have compounded these challenges, reducing cattle availability and higher consumer prices. As the summer grilling season approaches, consumers should anticipate continued price increases and consider alternative protein sources or budget adjustments to accommodate these changes.
Drought and Herd Reduction: Core Causes
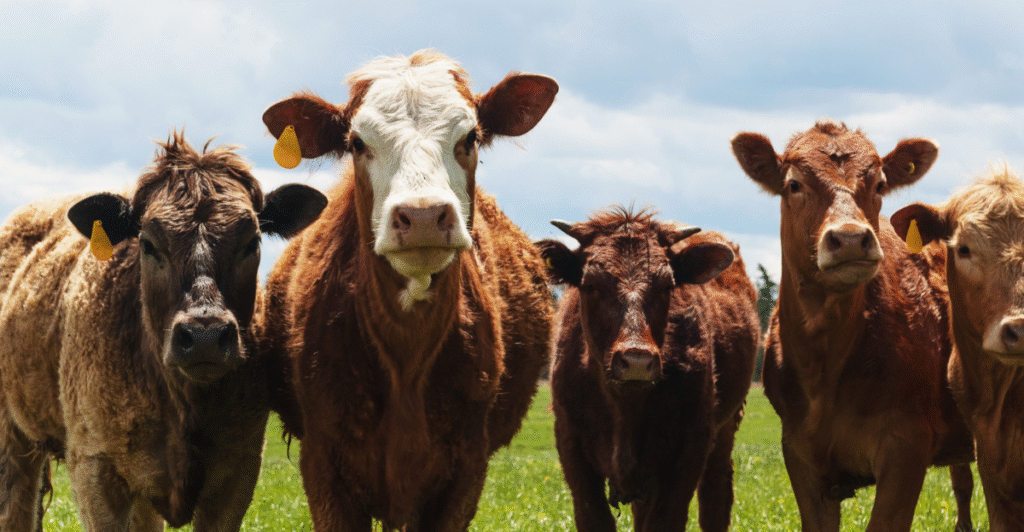

The Western U.S. has experienced prolonged drought conditions, severely impacting grazing lands and water resources essential for cattle rearing. Consequently, ranchers have been compelled to reduce herd sizes, leading to the smallest cattle inventory in over 70 years.
This reduction has created a supply-demand imbalance, driving up beef prices. Moreover, rebuilding herds is time-consuming, often taking up to 42 months to raise beef-ready steers, suggesting that high prices may persist in the foreseeable future.
Trade Disruptions Amplify Price Pressures
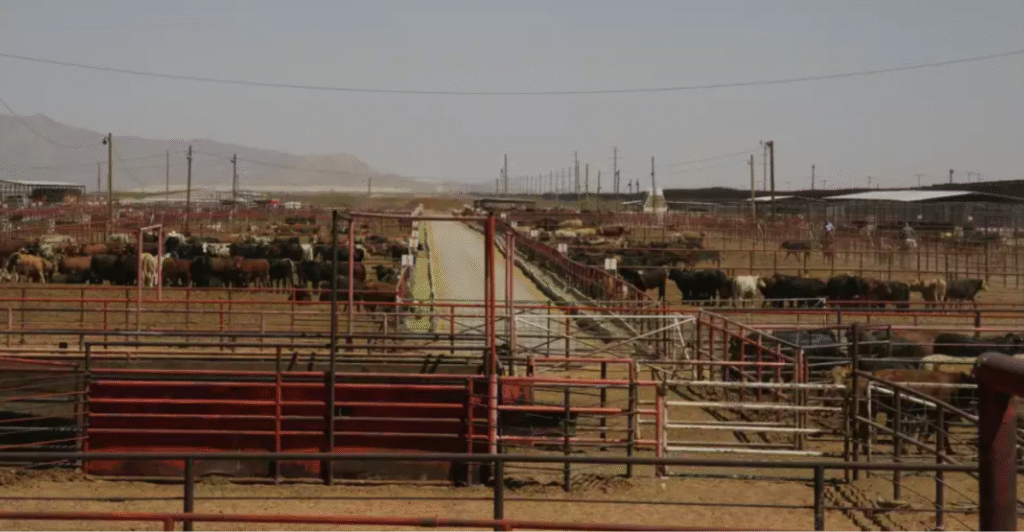

International trade dynamics have further exacerbated beef price inflation. Tariffs imposed on beef imports from key partners like Mexico, Brazil, and Canada have disrupted supply chains and increased costs.
Health concerns, such as the screwworm outbreak in Mexico, have also led to temporary suspensions of livestock imports, further tightening U.S. beef supplies. These factors collectively contribute to the escalating prices faced by American consumers.
Consumer Demand Remains Resilient
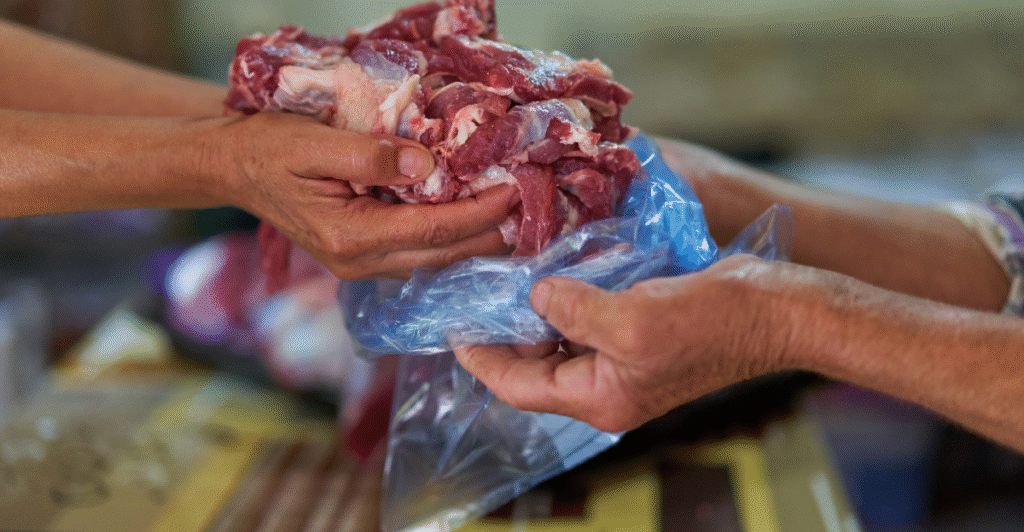

Despite rising prices, consumer demand for beef has remained robust. In 2024, fresh beef retail sales surpassed $40 billion, accounting for over 55% of all fresh meat sales.
This strong demand persists even as consumers face economic uncertainties and higher food costs, indicating a continued preference for beef products in American diets.
Retailers and Restaurants Adapt Strategies

Retailers and restaurants are implementing strategies to mitigate the impact of rising beef prices. For instance, Lidl U.S. has launched a private-label meat line, “Butcher’s Specialty,” offering high-quality, affordable cuts to attract budget-conscious shoppers.
Similarly, Texas Roadhouse has increased revenue by 10% through modest menu price adjustments and a focus on quality offerings, demonstrating adaptability in a challenging market.
Alternative Proteins Gain Popularity

As beef prices climb, consumers are increasingly turning to alternative protein sources. Chicken and pork have become more attractive options due to their relative affordability.
Tyson Foods reported a shift in consumer preference towards chicken, which helped offset a $181 million decline in beef sales over six months. This trend suggests a diversification in protein consumption patterns among Americans.
Economic Implications and Inflation

The surge in beef prices contributes to broader inflationary pressures within the U.S. economy. According to the USDA, beef and veal prices increased 8.6% from March 2024 to March 2025, outpacing general food inflation rates.
This escalation affects household budgets, particularly for families regularly consuming beef, underscoring the interconnectedness of agricultural markets and overall economic health.
Long-Term Outlook: Prices to Stay Elevated
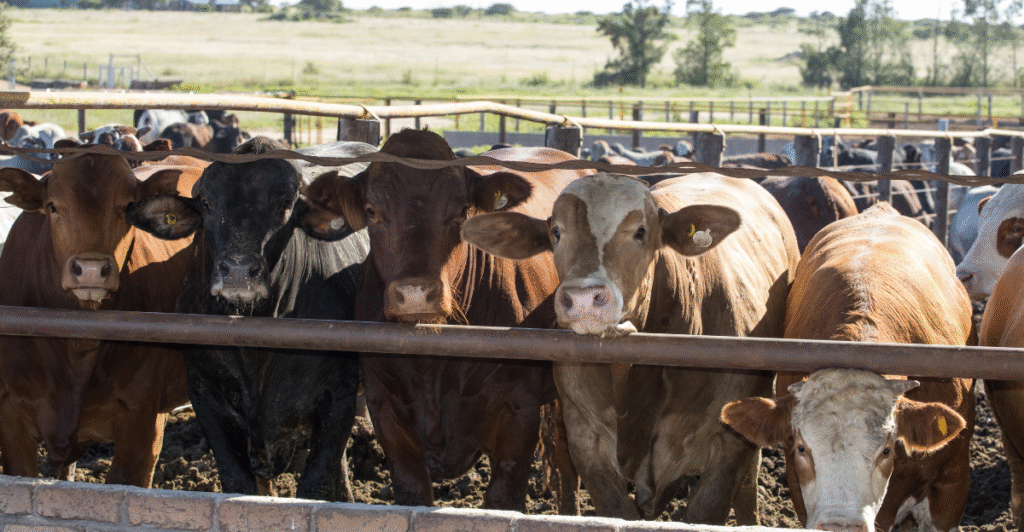

Experts predict beef prices will remain high through 2025 and potentially into 2026. The USDA projects a 6.3% increase in beef and veal prices for 2025, driven by tight supplies and sustained consumer demand.
Given the time required to rebuild cattle herds and the ongoing challenges in the supply chain, consumers should prepare for continued elevated prices in the near term.
Consumer Strategies for Coping

With beef prices at historic highs, consumers adapt by changing how they shop and eat. Many choose more affordable proteins like chicken, pork, or plant-based alternatives to cut costs. Buying beef in bulk during sales and freezing portions has become a popular strategy for stretching budgets.
Others select cheaper cuts such as ground beef or chuck, which remain flavorful when cooked properly. Cooking methods like slow roasting or marinating enhance taste without needing premium cuts. Shoppers also take advantage of grocery store promotions and loyalty programs to help offset rising meat prices.
Broader Economic Impact on American Finances

The escalation in beef prices reflects broader economic trends affecting American finances. As essential goods become more expensive, households may need to adjust spending habits, potentially reducing discretionary expenditures.
Moreover, if inflation persists, it could influence monetary policy decisions, affecting interest rates and borrowing costs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for consumers and policymakers as they navigate the economic challenges of rising food prices.
Discover more trending stories and Follow us to keep inspiration flowing to your feed!
Craving more home and lifestyle inspiration? Hit Follow to keep the creativity flowing, and let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
