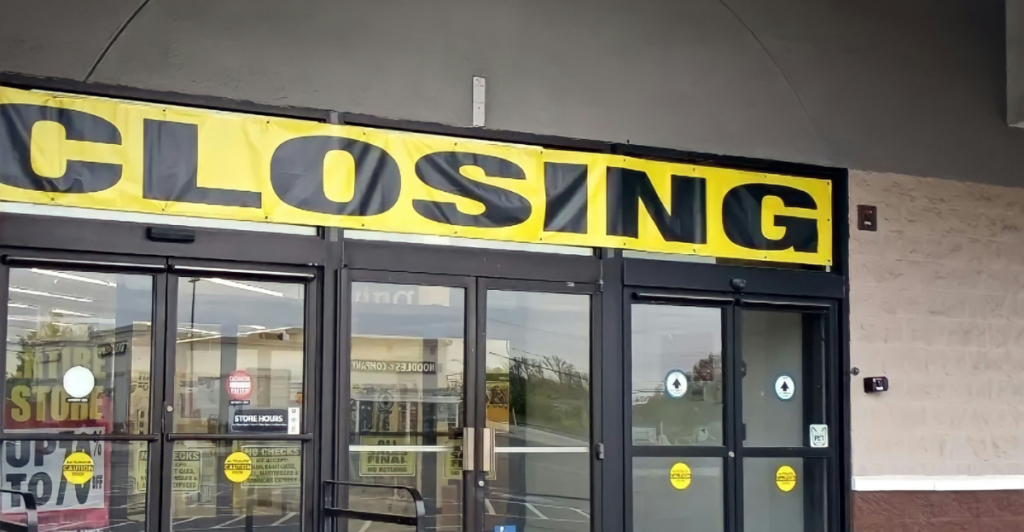

After four decades of serving families and individuals in Connecticut and Western Massachusetts, the iconic pet store, Smithland Pet & Garden Centers, has decided to close all 13 of its locations. The beloved retailer, which is famous for its expert advice and friendly service, has been around since 1985.
Over the years, Smithland’s store has provided its loyal customers with everything from pet food to gardening supplies, becoming a familiar destination for generations of families and their pets. The company’s decision to close all of its stores marks the end of an era for local communities that have relied on Smithland for important products and a sense of neighborhood connection.
The Announcement That Shocked Loyal Customers

Smithland’s leadership announced that these stores would be closing on May 5, 2025, through a press release and emails sent to its rewards card members. After recent challenges, CT Gardens LLC, the pet store’s parent company, has decided to liquidate the business. CT Gardens LLC’s CEO, John Atkins, said it was a “difficult” decision, and expressed appreciation for the many years of support from loyal customers.
A Statement
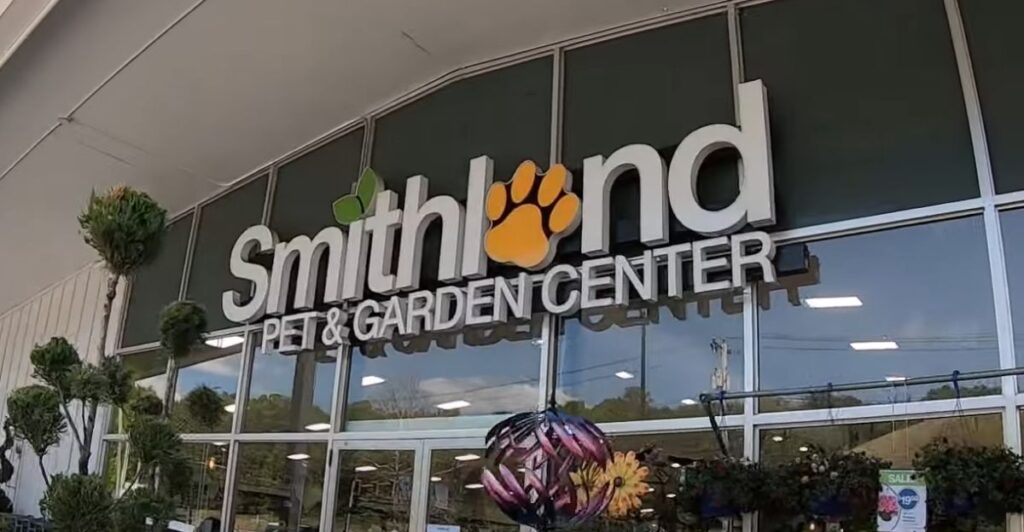

“Since 1985, Dave’s Soda and Pet City, myAgway, and Smithland have been more than a place to shop,” Atkins said in a statement. “They’ve been places where pets were pampered, gardens were grown, wild birds were fed, and neighbors became friends.” The news of these closures shocked loyal customers.
End of June Closures

The announcement revealed that all 13 stores, seven of which are in Connecticut and six in Massachusetts, will be closing by the end of June. Many regulars were surprised and saddened by the news. Smithland has become more than just a store for its loyal customers; it is a community hub for pet owners and gardeners.
The Roots of Smithland’s Legacy

Smithland first appeared in 1985 and was originally under the banners of myAgway and Dave’s Soda and Pet City. These stores had been quite successful since their early days. As the years passed, myAgway and Dave’s Soda and Pet City merged together and formed Smithland, expanding their products to include bird seeds, outdoor furniture, and much more.
Personalized Services

The Massachusetts locations, which were once known as Dave’s Soda and Pet City, were famous for their personalized service. As Smithland grew and adapted to meet its customers’ evolving needs, it always remained committed to its core passions: pets, gardening, and backyard living.
A Trusted Source

“Our 13 locations have become the trusted source for customers seeking lawn, garden, and pet supplies, along with competitive pricing and expert in-store advice. Smithland Pet Centers in Massachusetts, formerly known as Dave’s Soda & Pet City, employ the same inventory and staff from its previous incarnation, and generations of customers continue to entrust us with their pets’ health and well-being,” the company says on its website.
Economic Headwinds and Online Competition

The store decided to close all of its locations because of mounting economic pressures and tough competition from online retailers. Factors like inflation, increased expenses, and the challenges of the post-pandemic retail environment have made it harder for Smithland to stay competitive.
Brick-And-Mortar Stores

In recent years, online giants like Amazon and Chewy have taken over by offering convenience and lower prices, drawing customers away from traditional brick-and-mortar stores. This change in consumer habits, combined with supply chain challenges, ultimately became too much for Smithland to overcome. As shoppers gravitate toward the convenience, speed, and affordability of online retailers, brick-and-mortar stores are struggling to keep their doors open.
Closing Locations

Smithland will be closing seven Connecticut locations, including Bethel, Manchester, Middlefield, North Branford, North Haven, Old Saybrook, and Southington, and six more in Massachusetts, including Agawam, Hadley, Ludlow, Northampton, Ware, and Westfield. These closures will be felt deeply in the neighborhoods they served for the past few years.
The Impact on Local Communities

Smithland is famous for its knowledgeable staff, personalized recommendations, and the sense of community fostered within its stores. Many customers were shocked when they heard the news, noting how Smithland had become a regular stop because of their pricing and product selection. The loss of this iconic store leaves a gap in local retail, especially for people who value in-store advice and support for their pets and gardens.
A Challenging Time

These closures come at a difficult time for customers who are preparing for the spring gardening season. Many of Smithland’s loyal customers were surprised by the announcement, as they thought the store was doing well. One noted, “It’s shocking because you see there are so many people here on a regular basis. It’s crazy, especially with how good their pricing is.”
The Final Sales and Store Liquidation

Wanting to thank its loyal customers after so many years of service, Smithland launched a Customer Appreciation Sale from May 6 to 11. During this sale, they offered discounts on all non-sale items. This event, overlapping with the annual Mother’s Day sale, precedes the full liquidation of inventory.
Managing The Closures

All items purchased after May 6 are final sale, and gift cards are no longer available. The Smithland Rewards program will also end on May 12, 2025. The company is working with Hilco Consumer-Retail to manage the closing process and ensure a smooth transition for the staff and customers. Customers are not the only ones being affected by these closures; employees and suppliers will also be affected. Many staff members have served their communities for years, developing close relationships with some of the regulars.
Closing Voluntarily
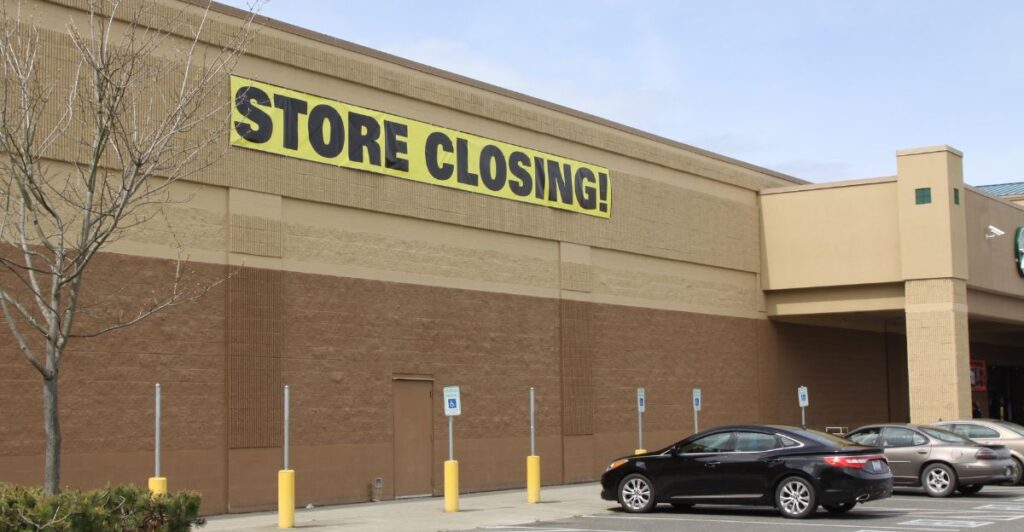

Vendors will also be affected, as they face the loss of a longstanding retail partner. The decision to close voluntarily rather than file for bankruptcy was made to preserve everyone involved’s dignity, including employees, customers, and partners. This approach allows for a more respectful and organized closing process, which helps avoid disruption and ensures a smoother transition during a difficult time.
Reflections from Leadership and Founders

CT Gardens LLC’s CEO, John Atkins, and Dave Ratner, the former owner of the store, have expressed their deep appreciation for the community’s support over the years. Atkins spoke about the trust and loyalty shown by customers, while Ratner, who led Dave’s Soda and Pet City for over 30 years, recalled the stores’ roles as gathering places for pet owners and gardeners.
Financial Impacts

The closure of Smithland Pet & Garden Centers, which has been a cherished retail institution in Connecticut and Massachusetts, will have significant financial impacts on the local communities it served for so many years. As all 13 locations shut down, many regular customers are losing trusted shopping experiences, personalized service, and community connections.
Added Expenses

For families and pet owners who depended on Smithland’s expertise and affordable pricing, the closures could bring added expenses and the inconvenience of moving to larger, less personal online retailers. Additionally, the closure will place a financial burden on employees and suppliers, adding to the growing trend of local businesses struggling to compete in an increasingly digital retail environment.
The Broader Retail Landscape

These closures are part of a larger trend that is currently affecting brick-and-mortar retailers across America. Many local chains are struggling due to economic uncertainty, changing consumer preferences, and the rise of e-commerce. Smithland’s experience reflects what many regional stores are currently facing. They are being forced to adapt or close as the industry changes around them.
A Community Says Goodbye

Smithland’s final days are approaching, and customers are flocking to stores for last-minute deals and to say goodbye to the iconic store. The iconic store’s closure marks the end of an era in New England retail, but its impact will endure in the memories of those it served. Smithland’s legacy is one of community, care, and connection, serving as a reminder of what local businesses bring to our lives.
Discover more trending stories and Follow us to keep inspiration flowing to your feed!
Craving more home and lifestyle inspiration? Hit Follow to keep the creativity flowing, and let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
