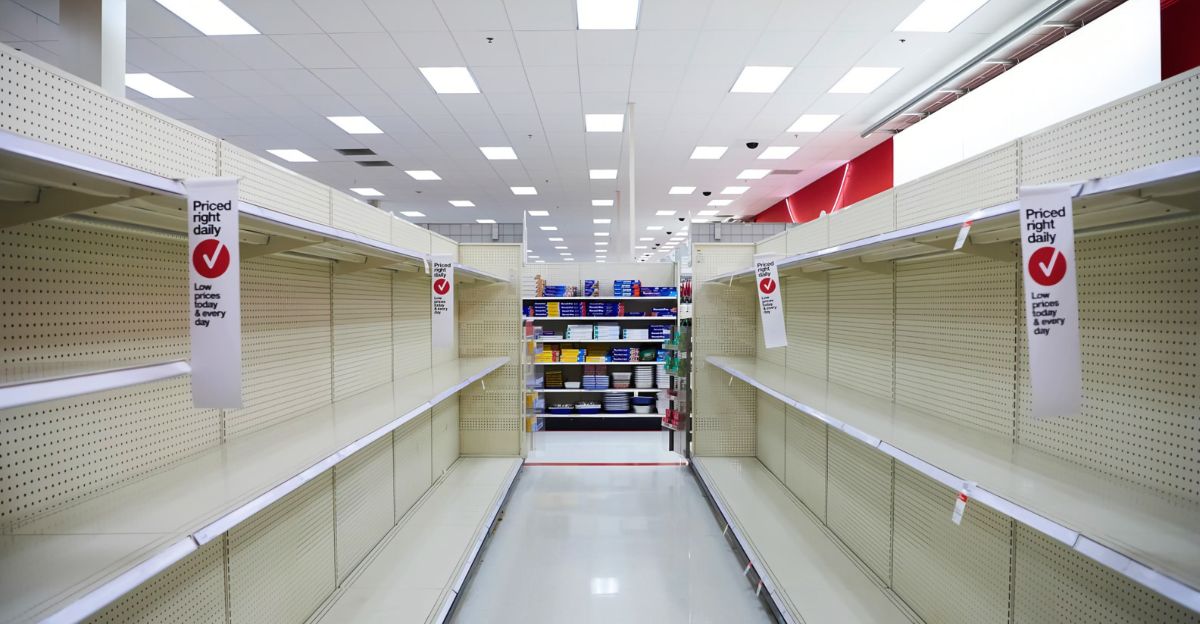

Another shock: China’s sudden cancellation of yet another wave of shipments to the United States in 2025 is a shock to American retail, not just a hiccup in the supply chain. Few understand the full impact of trade tensions and tariffs, which make headlines, as millions of containers disappear from ports, leaving shelves empty and logistics networks in disarray.
Fast fashion and electronics were particularly hard hit by these cancellations, highlighting the issues with relying too heavily on foreign suppliers. We can see how closely customer needs, store survival, and global politics are intertwined in today’s divided world when we examine which stores are having the most difficulties and why.
1. The First Casualties of Shipping Disruptions
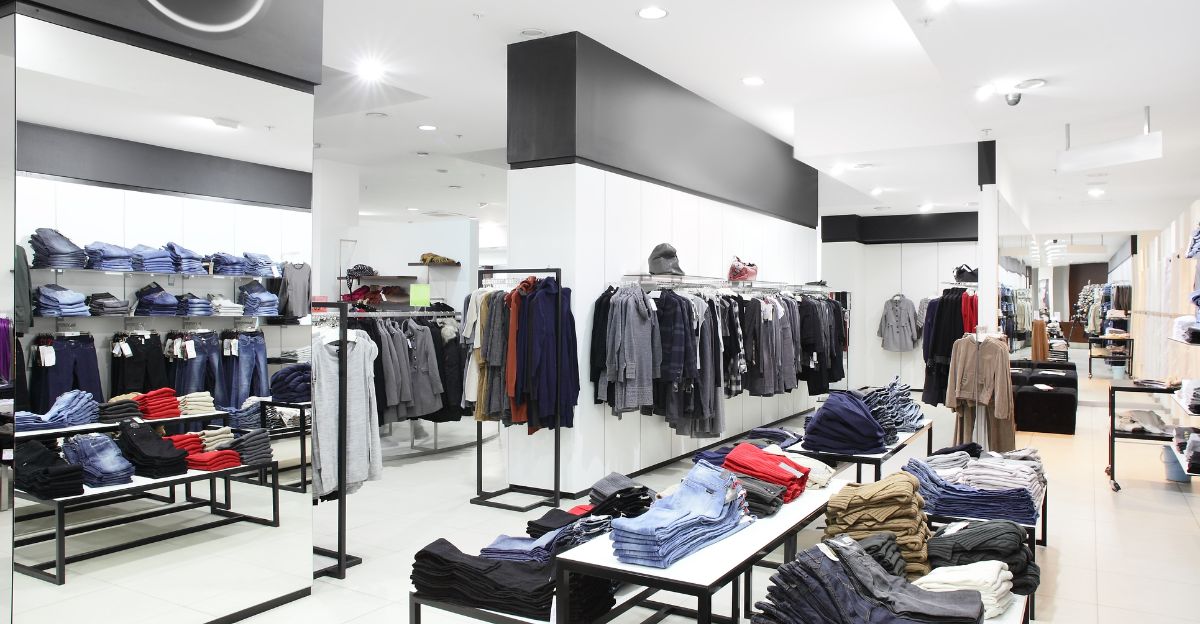

With reservations in the apparel and textile industries falling by more than 50%, these retailers are among the most severely impacted by China’s shipment cancellations. As seasonal demand peaks, fast fashion brands, which rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing, face inventory shortages.
These stores are forced to look for alternate suppliers or risk empty racks due to the abrupt decline in container availability and tariff-induced cost increases. Profits and customer loyalty are at risk during crucial selling windows as a result of this disruption, which highlights the weakness of “just-in-time” inventory models and the danger of becoming overly dependent on one sourcing nation.
2. Complex Supply Chains Under Pressure
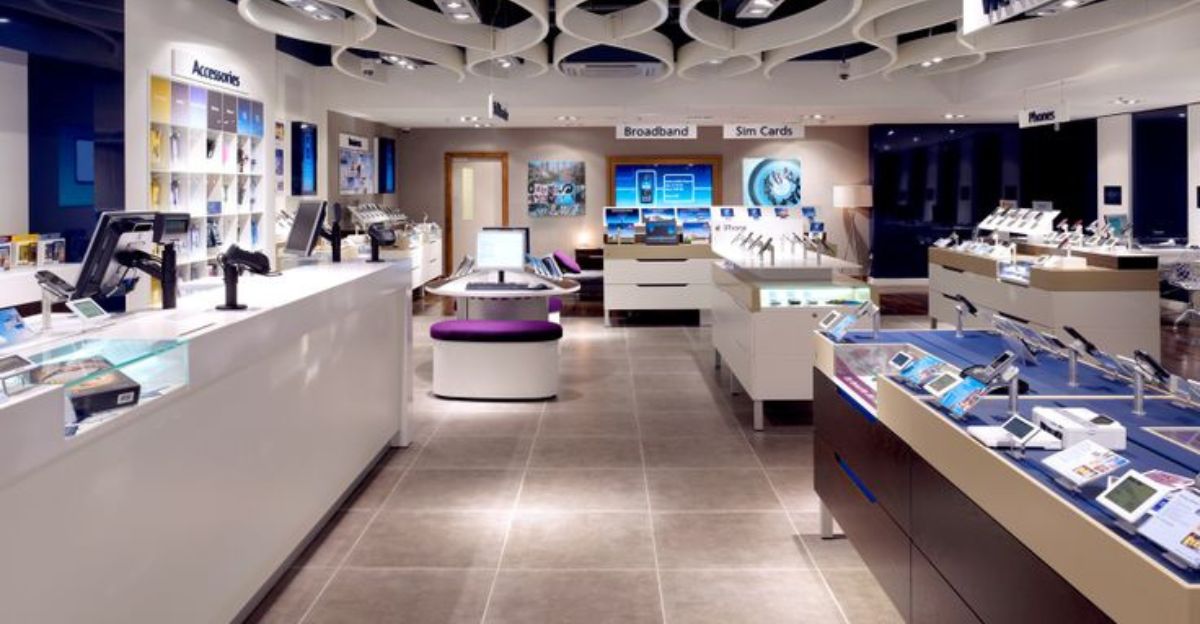

Despite certain tariff exemptions, electronics retailers are dealing with the ripple effects of cancellations on shipments. China-sourced components are delayed, which affects assembly lines all over the world. Major U.S. companies dominate the container trade, retailers like Amazon and Walmart, which report major disruptions in product availability.
As an example of how interconnected global supply chains intensify geopolitical shocks, the cancellations worsen already-existing chip shortages and logistics bottlenecks. It is difficult to maintain robust supply chains and low costs in the high-tech world of today due to difficulties in the sector.
3. Home Goods and Furniture
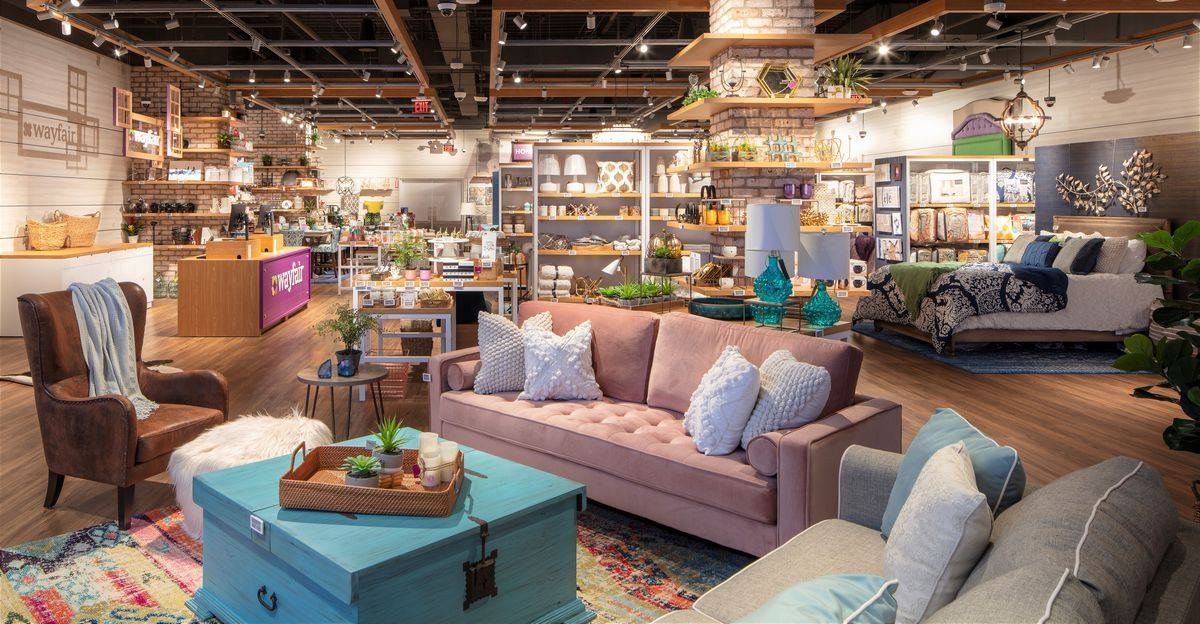

Retailers of furniture and home goods, frequently disregarded in trade talks, silently suffer from shipment cancellations. Many products rely on Chinese production for their final products or raw materials. Unexpected vessel cancellations are straining port operations and inland transportation due to container traffic being reduced by hundreds of thousands of TEUs.
These interruptions result in delivery delays and inventory shortages, which irritate clients and raise expenses. The industry’s predicament shows how trade disruptions affect everyday consumer necessities, regional economies that depend on port activity, and headline industries.
4. When Online Convenience Meets Physical Constraints

Shipment volumes from China have sharply decreased by about 50% since mid-April 2025 for e-commerce platforms, which were previously believed to be immune due to digital agility.
Low-value imports have decreased due to the termination of the de minimis exemption and tariff increases, which have forced cargo charter cancellations and slowed parcel flows. This calls into question the notion that traditional supply chain e-commerce can help avoid interruptions.
In a new era of limited international trade, online retailers must reconsider their sourcing strategies and customer expectations as reduced air and sea freight capacity threatens delivery speed and product assortment.
5. Grocery and Specialty Food Stores

Due to shipment cancellations, specialty food retailers who depend on Chinese imports, such as teas, spices, and packaged snacks, face particular difficulties. Seasonal and perishable goods must be purchased at the right time; otherwise, they may spoil or lose out on sales.
The interruption demonstrates how readily global political unrest can impact food supply chains.As a result, customerss may pay mort, and fewer food options may be available. The difficulties facing this sector demonstrate that trade disputes threaten not only goods like electronics or car, but also the safety of the American food supply and the variety of foods we enjoy.
6. The Domino Effect of Reduced Shipments

Cancelled voyages are causing significant drops in container traffic at ports on the U.S. East Coast, Gulf Coast, and West Coast. Reduced crane operations and lower demand for trucks and rail directly affect local economies, which impacts jobs in transportation, warehousing, and logistics in the thousands.
The idea that ports are immune to trade disputes is called into question by this economic downturn. Local tax income and job decreases reflect the impact these tense trading relations can create between the two nations at the expense of the U.S on communities.
7. The Psychological Toll on Retailers and Consumers
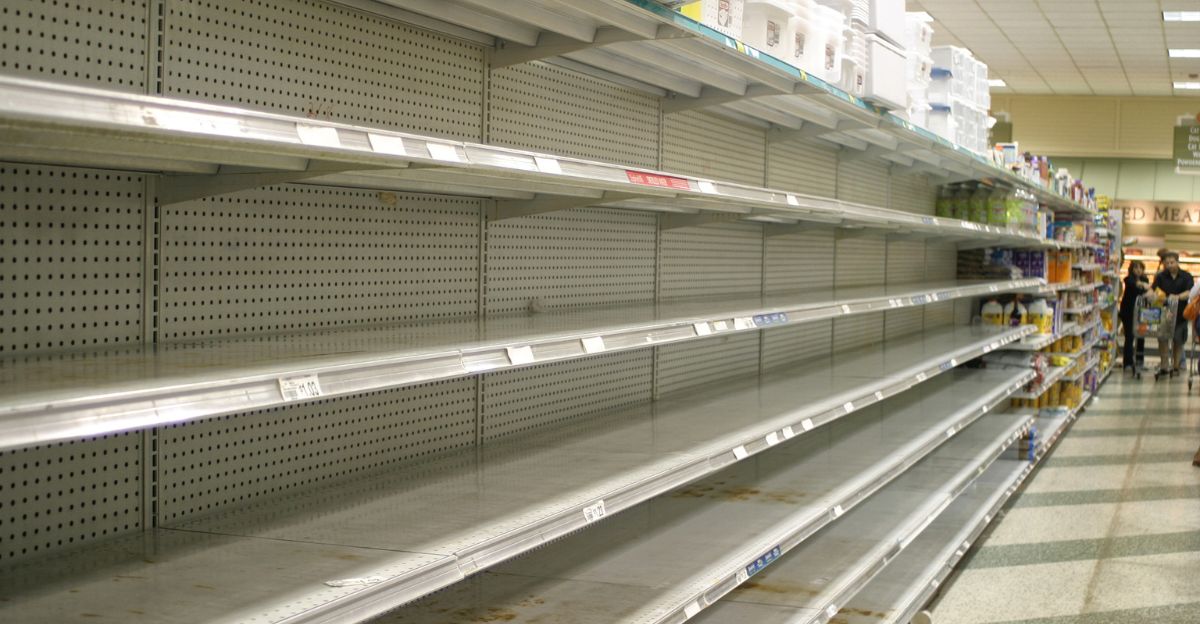

Beyond merely delivery problems, shipment cancellations cause anxiety and uncertainty for consumers and merchants. While customers deal with empty shelves and delayed deliveries, retailers must make impossible decisions about balancing inventory shortages against growing costs.
More companies are moving toward reshoring or diversifying their supply chains as a result of this breakdown in trust. It also exacerbates concerns about inflation and the stability of the economy.
The stress that people experience demonstrates why it’s crucial to maintain composure and have open discussions when things get difficult. It reminds us that actual people experience the consequences of the data by giving trade numbers a human face.
8. Could These Disruptions Accelerate Supply Chain Resilience?

Even though they are challenging, China’s shipment cancellations are forcing long-overdue adjustments in supply chains. In an effort to lower future risks, retailers are now acting by implementing nearshoring and local manufacturing.
The long-standing just-in-time global sourcing model has been upended by this disruption, which could result in stronger but more expensive supply chains. Because this change requires a significant investment of time and money, not all retailers will survive it. The crisis may therefore change the retail landscape by increasing the disparity between small enterprises and larger, better-funded firms that are better able to adjust.
9. Navigating the Fallout and Preparing for a New Trade Reality

Shipment cancellations by China are a wake-up call to remind us that international trade is both an economic engine and a geopolitical chessboard. From specialty foods to fast fashion, the hardest-hit retailers are vulnerable to systemic risks in fragile logistics networks and overconcentrated sourcing.
Consumer annoyance, job losses in port cities, and inventory shortages are some immediate effects; however, adjusting to a multipolar trade environment is more difficult. Retailers must invest in resilience, diversify their supply chains, and be open and honest with their customers. During this transition, policymakers should balance trade diplomacy with domestic economic protections to lessen future shocks.
Discover more trending stories and Follow us to keep inspiration flowing to your feed!
Craving more home and lifestyle inspiration? Hit Follow to keep the creativity flowing, and let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
